📌 TOPINDIATOURS Eksklusif ai: Adobe Research Unlocking Long-Term Memory in Video W
Video world models, which predict future frames conditioned on actions, hold immense promise for artificial intelligence, enabling agents to plan and reason in dynamic environments. Recent advancements, particularly with video diffusion models, have shown impressive capabilities in generating realistic future sequences. However, a significant bottleneck remains: maintaining long-term memory. Current models struggle to remember events and states from far in the past due to the high computational cost associated with processing extended sequences using traditional attention layers. This limits their ability to perform complex tasks requiring sustained understanding of a scene.
A new paper, “Long-Context State-Space Video World Models” by researchers from Stanford University, Princeton University, and Adobe Research, proposes an innovative solution to this challenge. They introduce a novel architecture that leverages State-Space Models (SSMs) to extend temporal memory without sacrificing computational efficiency.
The core problem lies in the quadratic computational complexity of attention mechanisms with respect to sequence length. As the video context grows, the resources required for attention layers explode, making long-term memory impractical for real-world applications. This means that after a certain number of frames, the model effectively “forgets” earlier events, hindering its performance on tasks that demand long-range coherence or reasoning over extended periods.
The authors’ key insight is to leverage the inherent strengths of State-Space Models (SSMs) for causal sequence modeling. Unlike previous attempts that retrofitted SSMs for non-causal vision tasks, this work fully exploits their advantages in processing sequences efficiently.
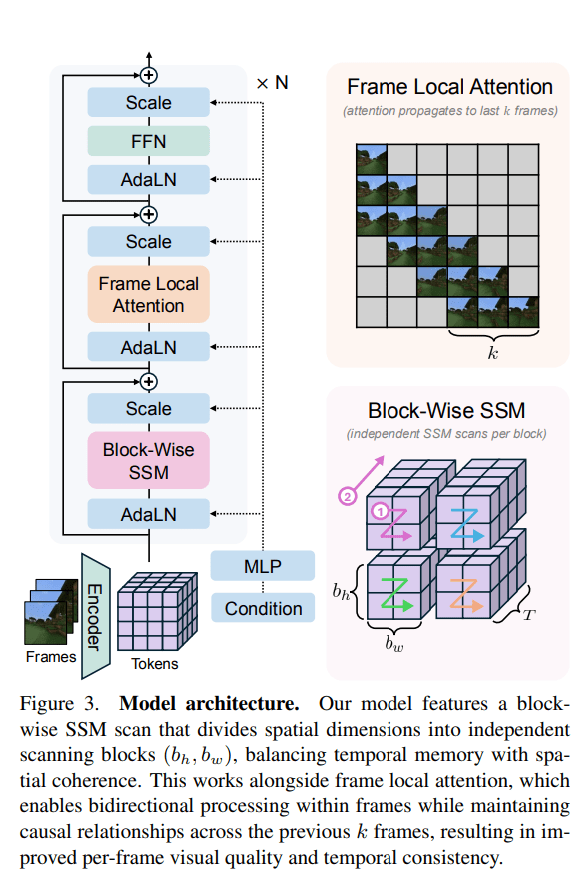
The proposed Long-Context State-Space Video World Model (LSSVWM) incorporates several crucial design choices:
- Block-wise SSM Scanning Scheme: This is central to their design. Instead of processing the entire video sequence with a single SSM scan, they employ a block-wise scheme. This strategically trades off some spatial consistency (within a block) for significantly extended temporal memory. By breaking down the long sequence into manageable blocks, they can maintain a compressed “state” that carries information across blocks, effectively extending the model’s memory horizon.
- Dense Local Attention: To compensate for the potential loss of spatial coherence introduced by the block-wise SSM scanning, the model incorporates dense local attention. This ensures that consecutive frames within and across blocks maintain strong relationships, preserving the fine-grained details and consistency necessary for realistic video generation. This dual approach of global (SSM) and local (attention) processing allows them to achieve both long-term memory and local fidelity.
The paper also introduces two key training strategies to further improve long-context performance:
- Diffusion Forcing: This technique encourages the model to generate frames conditioned on a prefix of the input, effectively forcing it to learn to maintain consistency over longer durations. By sometimes not sampling a prefix and keeping all tokens noised, the training becomes equivalent to diffusion forcing, which is highlighted as a special case of long-context training where the prefix length is zero. This pushes the model to generate coherent sequences even from minimal initial context.
- Frame Local Attention: For faster training and sampling, the authors implemented a “frame local attention” mechanism. This utilizes FlexAttention to achieve significant speedups compared to a fully causal mask. By grouping frames into chunks (e.g., chunks of 5 with a frame window size of 10), frames within a chunk maintain bidirectionality while also attending to frames in the previous chunk. This allows for an effective receptive field while optimizing computational load.
The researchers evaluated their LSSVWM on challenging datasets, including Memory Maze and Minecraft, which are specifically designed to test long-term memory capabilities through spatial retrieval and reasoning tasks.
The experiments demonstrate that their approach substantially surpasses baselines in preserving long-range memory. Qualitative results, as shown in supplementary figures (e.g., S1, S2, S3), illustrate that LSSVWM can generate more coherent and accurate sequences over extended periods compared to models relying solely on causal attention or even Mamba2 without frame local attention. For instance, on reasoning tasks for the maze dataset, their model maintains better consistency and accuracy over long horizons. Similarly, for retrieval tasks, LSSVWM shows improved ability to recall and utilize information from distant past frames. Crucially, these improvements are achieved while maintaining practical inference speeds, making the models suitable for interactive applications.
The Paper Long-Context State-Space Video World Models is on arXiv
The post Adobe Research Unlocking Long-Term Memory in Video World Models with State-Space Models first appeared on Synced.
🔗 Sumber: syncedreview.com
📌 TOPINDIATOURS Eksklusif ai: Elon Musk Says His Optimus Robot Is So Dope That Peo
Amid abysmal car sales that continue to plummet worldwide and major regulatory hurdles plaguing the company’s driver assistance software, Tesla CEO Elon Musk is desperately looking to reinvent the company.
His newfound obsession has been Tesla’s Optimus humanoid robot, an invention that he says will transform the EV maker into a $25 trillion robotics company. He’s promised that Optimus will account for the vast majority of the company’s already extremely inflated value — a claim he’s now taking to an extraordinary new extreme.
Responding to a clip of entrepreneur and investor Jason Calacanis claiming during a recent summit that “nobody will remember that Tesla ever made a car” and that “they will only remember” the company building “a billion” Optimus robots, Musk had a sweeping prediction.
“Probably true,” he replied.
Beyond once again demonstrating Musk’s penchant for making vastly exaggerated claims about his companies, the admission neatly summarizes what we’ve suspected for quite some time now: Tesla and Musk are ready to move on from the EV and are looking to capitalize on the next big hype cycle.
Tesla still has a lot to prove when it comes to its bipedal assistant. As part of Musk’s $1 trillion pay package, the company will need to deploy one million Optimus robots, a goal the mercurial CEO has promised could be achieved by 2030.
Reality, however, has plenty of catching up to do. The company has encountered major technical snags in its efforts to build out production lines and reportedly failed to keep up with its own stated goal of building 5,000 Optimus robots last year.
The company’s demos have also fallen far short of expectations, with one robot struggling to walk down a clear office hallway. Tesla is also still heavily relying on teleoperators, suggesting that autonomous operation without the need for a human pilot could still be a long way out.
In short, Musk’s extremely boisterous claims that “Optimus will eliminate poverty and provide universal high income for all” should be taken with a grain of salt.
For now, investors in the EV firm are happily buying into the CEO’s vision. The stock hit an all-time closing high of just shy of $500 in mid-December. That’s despite Tesla still facing declining deliveries and sales as it desperately attempts to reinvent itself as a humanoid robotics company.
More on Optimus: Amazing Video Shows Tesla Optimus Teleoperator Taking Off Headset, Causing Robot to Stumble and Collapse
The post Elon Musk Says His Optimus Robot Is So Dope That People Will Forget Tesla Ever Made Cars appeared first on Futurism.
🔗 Sumber: futurism.com
🤖 Catatan TOPINDIATOURS
Artikel ini adalah rangkuman otomatis dari beberapa sumber terpercaya. Kami pilih topik yang sedang tren agar kamu selalu update tanpa ketinggalan.
✅ Update berikutnya dalam 30 menit — tema random menanti!