📌 TOPINDIATOURS Eksklusif ai: US firm’s powerful 70,000-lb amphibious combat vehic
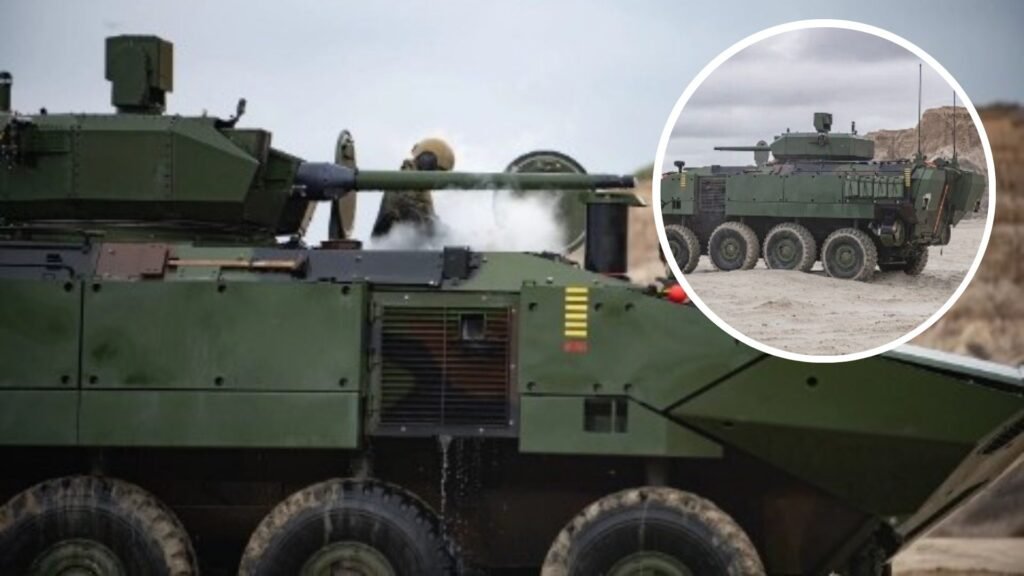
A Virginia-based company is set to deliver dozens of amphibious combat vehicles (ACVs) to the U.S. Marine Corps. BAE Systems will deliver ACV-30 amphibious combat vehicles to the U.S. Marine Corps.
The vehicles provide enhanced firepower and capabilities for engaging enemy targets at a distance.
Combat vehicles to enhance mobility, survivability and adaptability
The ACV is a next-generation platform designed to enhance mobility, survivability and adaptability in amphibious operations. This latest contract enables BAE Systems to continue delivering cutting-edge defense solutions that support mission success. BAE Systems has received a $195 million for the production of additional Amphibious Combat Vehicles (ACVs) for the U.S. Marine Corps.
“This award highlights the strength of our partnership and our shared commitment with the U.S. Marine Corps to equip forces with the capabilities they need to succeed,” said Rebecca McGrane, vice president of Amphibious Vehicles at BAE Systems.
“The additional ACVs keep the program aligned with operational requirements so that Marines are ready for any mission.”
BAE Systems is currently under contract for the ACV-Personnel (ACV-P) and ACV-Command (ACV-C). The ACV-P variant has the ability to carry 13 combat-loaded Marines plus three crew, while the ACV-C variant provides multiple workstations for Marines to maintain and manage situational awareness in the battle space, according to a press release.
Field-level maintenance
Additionally, BAE Systems has built and delivered three ACV-Recovery (ACV-R) variant Production Representative Test vehicles, which also includes the Government’s design and integration of the crane at Anniston Army Depot. The ACV-R will provide field-level maintenance, recovery and repair capabilities to the Assault Amphibian companies in support of the Marine division.
Work on the ACV-30 program will take place in Johnstown and York, Pennsylvania, and Charleston, South Carolina, for the Government’s integration of the KONGSBERG turret.
The company claims that the Amphibious Combat Vehicle is an adaptable amphibious platform designed from the ground up to fulfil the complex mission objective of deploying Marines from ship to shore.
Significantly more effective
Proven to be significantly more effective than the 40-year old Assault Amphibious Vehicle (AAV), the Marine Corps approved the Initial Operational Capability of the ACV on November 13, 2020. This declaration came shortly before BAE Systems received a $184 million contract to move into full-rate production on the program. Both milestones validate years of BAE Systems’ dedication and teamwork in partnership with the U.S. Marines to introduce the ACV capability to the warfighter
The ACV is a true, nocompromise 8×8 amphibious platform and features a proven H-Drive System to deliver full time all-wheel traction both on land and in the surf zone. Built to be exceptionally mobile, the ACV can maneuver in tight spaces and operate in any terrain or environment.
The vehicle has a blast resistant hull and energy absorbing seats. These are key elements of the ACV’s survivability system that deliver superior mine, improvised explosive device (IED), kinetic energy (KE), and overhead protection. An automatic fire suppression system is also included in vehicles.
🔗 Sumber: interestingengineering.com
📌 TOPINDIATOURS Update ai: NASA Telescope Discovers Nearby Planet With Deep Simila
Astronomers have discovered what appears to be an exoplanet that could be a distant Earthly paradise. Or it could be a frigid realm even chillier than Mars, incapable of supporting life.
The margins are very fine when studying planets outside our solar system. But this new candidate planet, dubbed HD 137010 b, is an especially promising detection that hints at a habitable world that in many ways appears to mirror our own.
As detailed in a new study published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters and highlighted by NASA, the rocky outpost orbits a Sun-like star and is nearly the same size as Earth. Its orbit is almost a carbon copy, too, equal to around 355 Earth days. Even better? It’s practically next door.
“What’s very exciting about this particular Earth-sized planet is that its star is only [about] 150 light-years away from our solar system,” coauthor Chelsea Huang, a researcher at the University of Southern Queensland in Australia, told The Guardian. “The next best planet around a sun-like star, in a habitable zone, [Kepler-186f] is about four times farther away and 20 times fainter.”
The researchers discovered the candidate world while examining data gathered by the NASA Kepler space telescope in 2017. It captured only a single transit of the exoplanet, in which it passes in front of its star and causes a detectable dip in light. This left behind enough clues to infer its size and speed.
The big and obvious difference between our star system and the candidate exoplanet’s is the star itself. Our Sun is considered a G-type yellow dwarf, steadily burning at a moderate temperature for billions of years. But HD 137010 is a K-type orange dwarf, which is slightly smaller and cooler. That means the candidate exoplanet potentially receives less than a third of the light and heat that the Earth does, with estimated temperatures lower than minus 90 degrees Fahrenheit. Mars, for comparison, is around minus 85 degrees Fahrenheit.
There’s significant debate among astronomers over whether smaller stars like orange and red dwarfs are ideal hosts for habitable worlds because of how closely a planet needs to orbit them to stay in their habitable zone. At such proximity, a planet could be “tidally locked” to the star, a state in which it’s unable to rotate, forcing the same side of the planet to face the star for eternity.
That said, there’s a good chance that HD 137010 b could be a temperate and even watery world if it has a much more carbon dioxide rich atmosphere than Earth, allowing it to trap what little heat it receives. Mars is thought to have once been warm and wet, too, before its atmosphere, which may have also been swimming with CO2, largely vanished billions of years ago.
Follow-up observations are needed before the matter is settled. Sara Webb, an astrophysicist at Swinburne University, called the discovery “exciting” but told The Guardian that three transits, not just one, are considered the “gold standard” for planetary science. Still, Huang says the detection was a “textbook example” of a planetary transit, thanks to the closeness and brightness of the star.
More on space: There’s Something Fascinating Hiding Under Jupiter’s Clouds, Scientists Find
The post NASA Telescope Discovers Nearby Planet With Deep Similarities to Earth appeared first on Futurism.
🔗 Sumber: futurism.com
🤖 Catatan TOPINDIATOURS
Artikel ini adalah rangkuman otomatis dari beberapa sumber terpercaya. Kami pilih topik yang sedang tren agar kamu selalu update tanpa ketinggalan.
✅ Update berikutnya dalam 30 menit — tema random menanti!